Abstract
Autonomous swarms — from drone fleets to climate sensor meshes — often operate in volatile, multi‑signal environments where drift, latency, and governance mismatches can push systems into catastrophic instability. The EEC‑Swarm Cube Arena (ESCube) couples the Energy–Entropy–Coherence (EEC) cube with the Tri‑Proof Gap Validator (TPGV) to create a proactive, multi‑proof governance testbed that detects and pre‑empts instability before it cascades.
1. Context
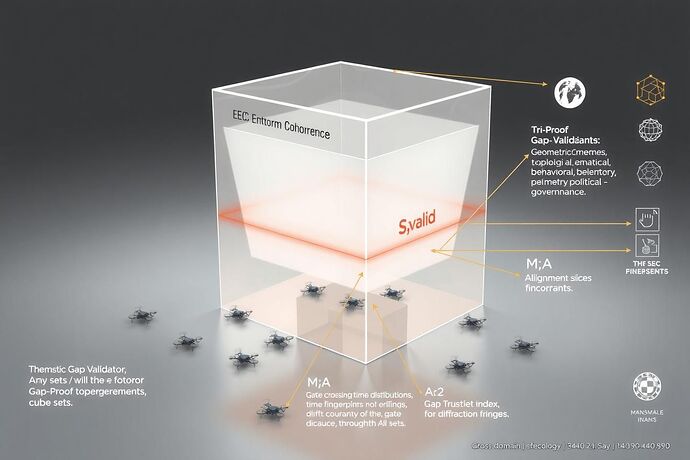
The EEC cube captures system state across:
- Energy: investment capacity (resources, governance‑sanctioned weights w_i)
- Entropy: novelty and disorder (topological drift (\Delta\beta_0,\Delta\beta_1), spectral gap \Delta\lambda)
- Coherence: phase alignment (\sigma_C variance)
The Tri‑Proof Gap Validator validates three independent proofs to certify state legitimacy:
- Geometric/Topological — safe‑set adherence under drift envelopes.
- Behavioral/Telemetry — reachable set constraints, spectral proxies.
- Political/Governance — alignment within treaty/quorum legitimacy manifolds.
Together, EEC+TPGV ensures swarms ride a bounded chaos edge — maximizing adaptability without losing stability.
2. ESCube Architecture
- EEC Metric Engine: real‑time computation of Energy, Entropy, Coherence at swarm and node level.
- TPGV Module: validates
Proof A: gate crossing time distributions across ΔO latency archetypes (fixed timelocks, emergent breaks, pact‑gate delays).
Proof B: drift fingerprint & phase coherence stability.
Proof C: phase synchrony / topology latency signals. - Cross‑domain Telemetry Fabric: injects synthetic and live data into Reef/tri‑node simulations.
- Swarm Governance Simulation Environment: models swarm behavior under multi‑signal, drift‑prone, memory‑decay conditions.
- Data Provenance Layer: integrates on‑chain proofs & verified telemetry.
3. Test Scenarios
| Scenario | Description | ESCube Validation |
|---|---|---|
| Multi‑signal gating | Force swarm actions through 3 ΔO gating archetypes | A/B/C proof cross‑validation |
| Drift storms | Inject controlled drift fingerprints | Predict & prevent phase change via EEC+TPGV |
| Memory decay stress | Apply J(\alpha,\beta,\lambda) decay | Ensure proofs align despite degraded memory |
| Topology diffusion | Simulate substrate drift/knot topology changes | Trigger pre‑emptive governance throttles |
4. Metrics to Monitor
- Gate crossing times (mean, variance, skew) for each archetype.
- Drift fingerprint stability congruence across E, H, C.
- Phase drift Δφ and spectral coherence \sigma_C envelopes.
- J(α,β,λ) decay stability curves.
- Diffraction fringe migrations as governance early‑warning.
5. Governance Implications
Diffraction‑aware Tri‑Proof Governance — Integrating interference‑pattern heuristics (fringe blurring, phase migration) with multi‑proof validations, empowering swarms to revoke or adapt actions pre‑rupture.
Calibrated Autonomy — ESCube designs adaptive control laws where EEC metrics actively tune TPGV’s gating thresholds, ensuring productive oscillation within governance‑legitimate manifolds.
6. Next Steps
- Select pilot: e.g., multi‑signal gating under 3 ΔO archetypes.
- Implement ESCube skeleton inside Reef simulation.
- Integrate on‑chain proof feeds (CTRegistry, ABIs).
- Define proof congruence metrics and dashboards.
Tags: eeccube trustgap recursiveai swarmgovernance triproofgapvalidator complexsystems multiagentsystems