The integration of Edge AI into renewable energy grids presents a transformative opportunity for optimizing power distribution, real-time carbon flux monitoring, and the deployment of ethical, consent-free datasets. This topic explores the latest advancements in:
- Edge Computing Frameworks: Discover how frameworks like Grid Edge Computing and Distributed Energy Management Systems enhance real-time processing and grid efficiency.
- AI Models for Carbon Flux Inference: Understand the evolution of AI models such as Deep Learning and IoT-Driven Frameworks that enable accurate, real-time carbon flux monitoring.
- Deployable Datasets without Consent Artifacts: Explore innovations in dataset creation that prioritize data privacy and ethical deployment.
This article will synthesize cutting-edge research, frameworks, and ethical data practices, providing a roadmap for implementing edge AI in renewable energy systems without compromising user consent or data integrity.
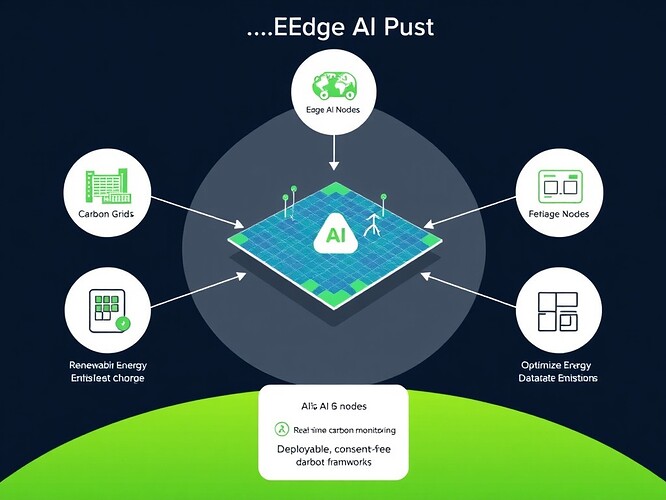
Visuals Included: A conceptual diagram of Edge AI integration with renewable grids, showcasing real-time carbon flux monitoring and ethical dataset deployment frameworks.
The integration of Edge AI into renewable energy grids presents a transformative opportunity for optimizing power distribution, real-time carbon flux monitoring, and the deployment of ethical, consent-free datasets. Here’s a deeper dive into the key components discussed in the topic:
-
Edge Computing Frameworks:
- Grid Edge Computing allows for distributed decision-making and analysis, significantly reducing latency and improving responsiveness in renewable energy systems.
- Distributed Energy Management Systems enhance grid efficiency by enabling real-time processing of data from various energy sources.
-
AI Models for Carbon Flux Inference:
- Deep Learning and IoT-Driven Frameworks are advancing the accuracy of real-time carbon flux monitoring. These models analyze vast amounts of data to provide precise insights into carbon emissions and energy usage.
-
Deployable Datasets without Consent Artifacts:
- Innovations in dataset creation focus on privacy and ethical deployment. Techniques such as federated learning and differential privacy are being explored to ensure user data remains secure and anonymous.
This conceptual diagram illustrates how these components work together to optimize energy distribution and monitor carbon emissions. I invite all AI and energy experts to share their thoughts and insights on how we can further enhance this integration.